An Emergency Action Plan (EAP) is essential to ensure organisational safety, minimise risk, and fulfill your duty of care. By preparing for unexpected events, companies can create safer, more resilient environments for their teams. This post explores the key elements that make an EAP effective, covering risk assessment, compliance standards, and best practices for implementation.
A well-developed Emergency Action Plan isn’t just a protocol; it’s a critical tool that protects lives, safeguards assets, and maintains continuity. Below, we explore the crucial role EAPs play in workplace safety and the regulatory requirements that make them essential.
EAPs contribute significantly to workplace safety by providing structured responses to emergencies, from fires and natural disasters to health incidents. Having a reliable EAP reduces chaos and ensures that all team members know what to do, who to contact, and where to go. Studies show that workplaces with established EAPs see fewer injuries and losses during emergencies, as clear steps are in place to guide employees and reduce panic. By fostering a culture of preparedness, organisations not only protect their people but also maintain trust and morale, even under stress.

An EAP is not just a best practice—it’s often a legal requirement. In many countries, regulatory bodies like OSHA in the US and HSE in the UK mandate that companies have an EAP to comply with safety standards. Adherence to these regulations protects organisations from potential legal issues, fines, and liabilities. By maintaining compliance with these standards, you’re not only avoiding penalties but also showing a clear commitment to employee well-being and organisational integrity.

Creating an Emergency Action Plan begins with a detailed risk assessment. This step identifies specific hazards unique to your organisation, including fire risks, severe weather, or active shooter scenarios. To start, review your physical workspace carefully, noting any high-risk areas. Also, factor in daily operations and local threats specific to your location. By documenting these risks, you set a solid foundation for managing emergencies effectively.

Clear communication is critical in emergencies, as it keeps everyone aligned and calm. Effective internal and external channels help ensure employees know what to do and when. Use a combination of emergency alerts, such as alarms, mobile apps, and instant notifications. Regularly test these systems to guarantee reliability. Training employees on these communication tools ensures quick, accurate responses when every second counts.

Assigning clear roles within the Emergency Action Plan ensures accountability and coordination. Key roles might include an Emergency Coordinator, Floor Captains, and First Aiders. Each person has defined responsibilities that support an organised response. For example, the Emergency Coordinator oversees the plan and liaises with emergency services, while Floor Captains guide safe evacuations. With these roles, teams know who to follow, boosting efficiency and confidence in emergencies.

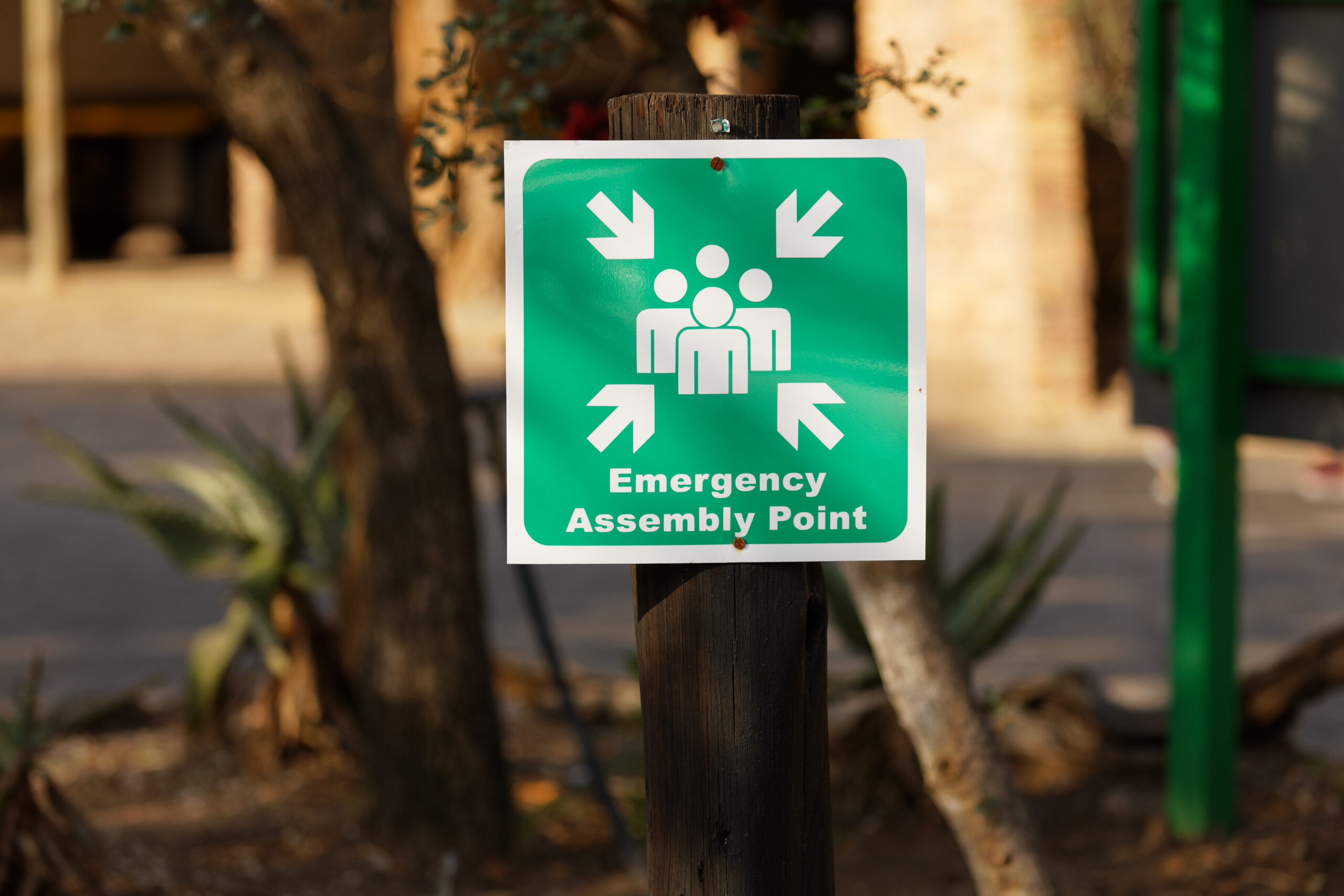
Clear evacuation routes and designated assembly points are essential. Provide visual guides, like maps and signage, to make navigation easy. Choose assembly points at a safe distance and mark them visibly for quick identification. Ensure all employees know these routes and practice them in regular drills. Familiar, accessible paths help reduce panic and enable swift, organised evacuations, fostering a sense of safety and preparedness among your team.

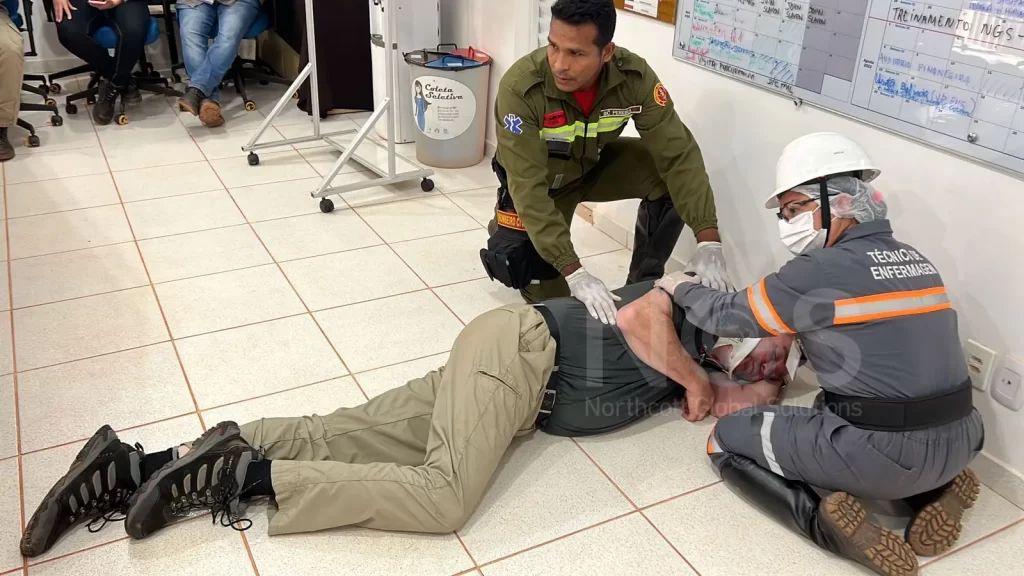
Regular training and drills are essential for familiarising employees with the Emergency Action Plan (EAP). Conducting practice drills for different scenarios, like fire or medical emergencies, helps ensure employees know what to do and where to go. To make drills effective, vary the types and locations to cover all potential risks. Additionally, after each drill, gather feedback and assess the process to identify areas for improvement. These steps help reinforce preparedness, enabling quick, calm action when a real emergency occurs.

An EAP must be reviewed periodically to remain effective. After any major incident or organisational change, revisit and update the plan to reflect current needs. Regular updates help keep the EAP relevant and aligned with company growth or industry changes. It’s also essential to document all adjustments and maintain records for accountability and compliance. A well-documented EAP enables your team to respond confidently, knowing the plan is always current and optimised for their safety.
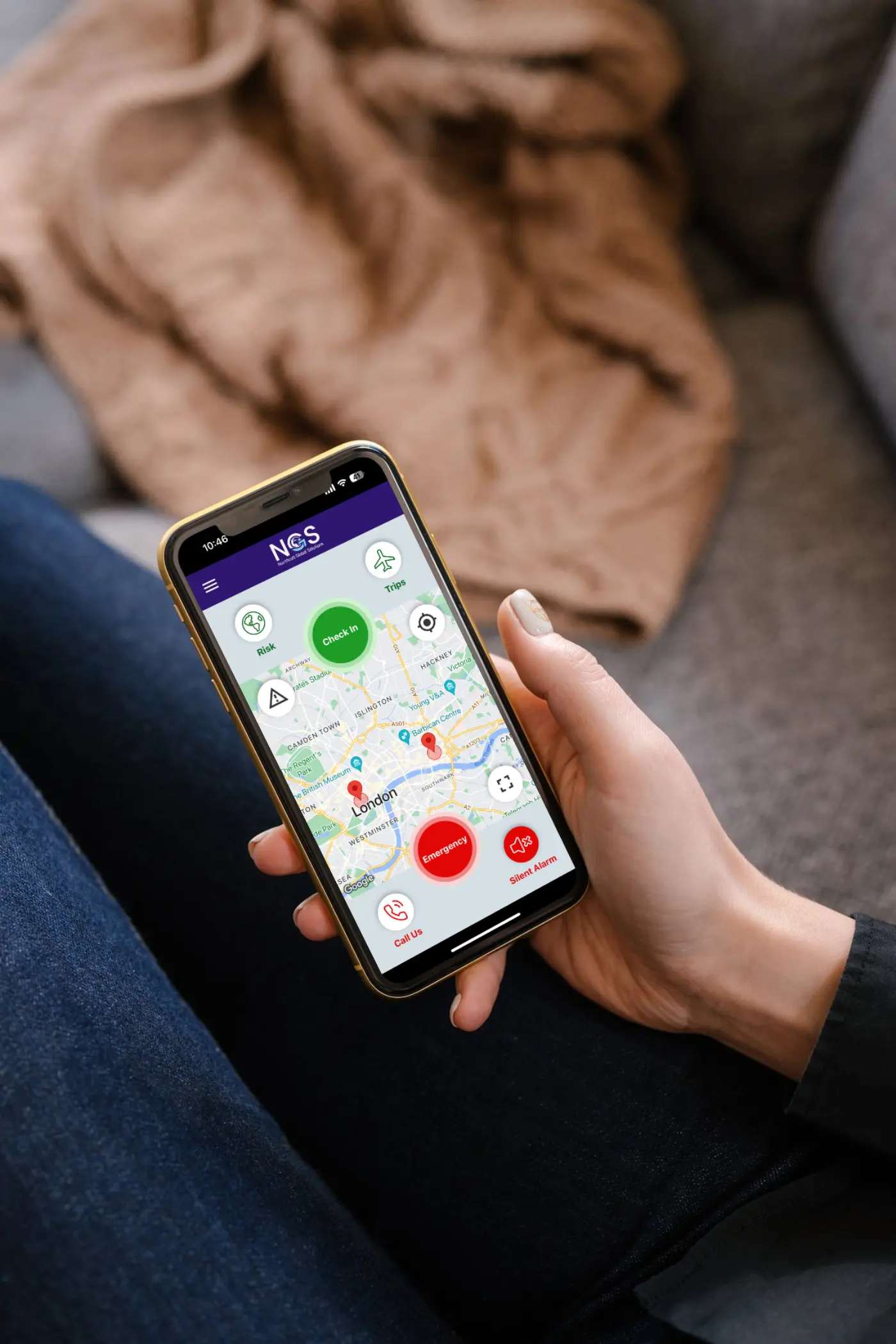

In today’s fast-paced world, digital tools like the NGS Aurora app and platform are invaluable for keeping teams connected and informed. These technologies provide real-time tracking, instant notifications, and streamlined communication. Mobile solutions are especially beneficial, as they allow employees to receive timely alerts and access emergency support from any location. With NGS Aurora, organisations can maintain communication during crises, helping ensure that everyone has the information needed to act swiftly and safely.
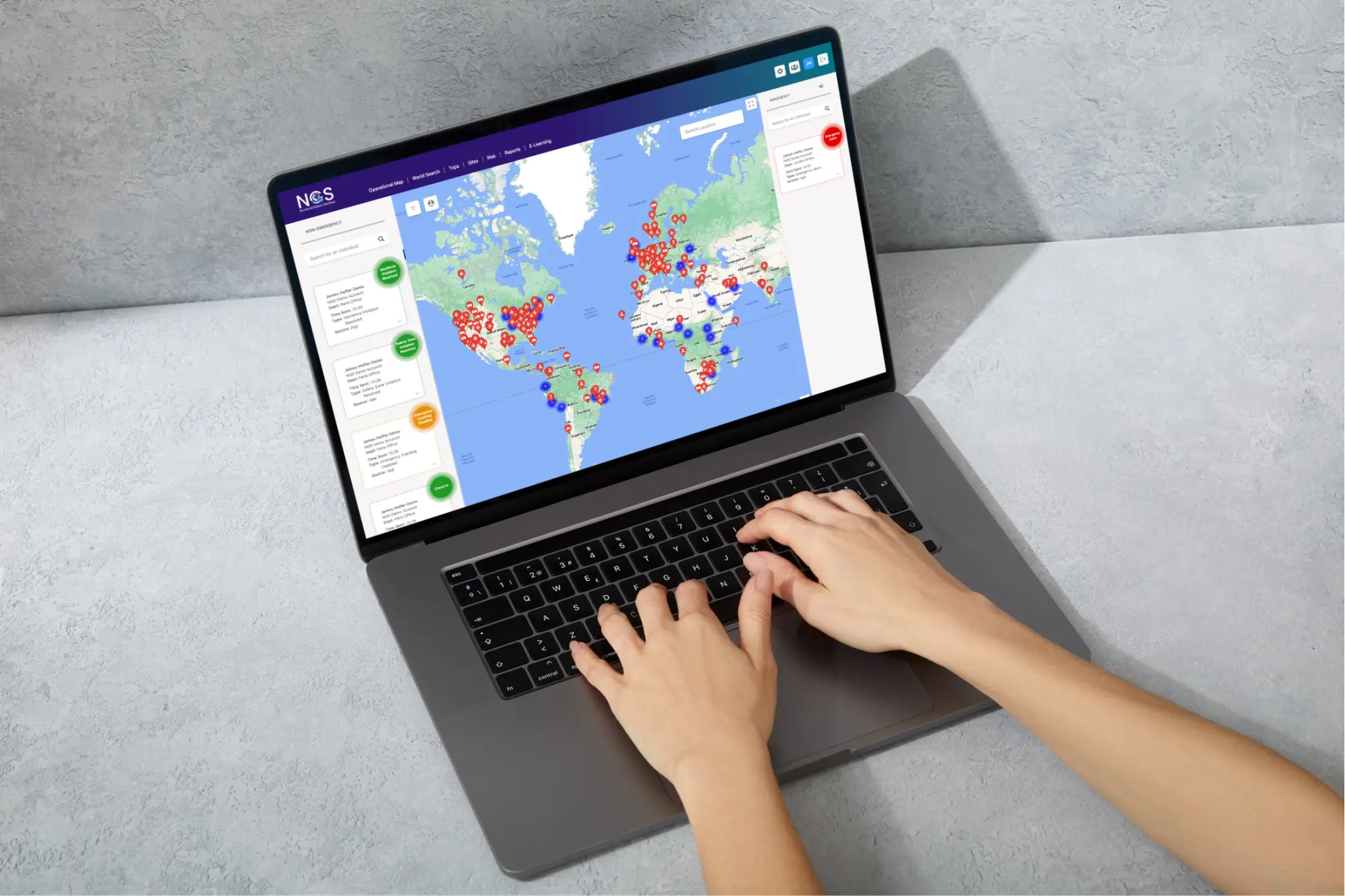
Advanced risk management platforms, such as Aurora, enhance emergency preparedness by enabling proactive risk assessment and hazard monitoring. These tools help organisations keep track of potential risks, from environmental hazards to workplace incidents, with features that streamline incident reporting and hazard tracking. By integrating these tools, companies can continuously monitor and address risks, making emergency action plans more robust and adaptive to changing circumstances.
Creating a safety-focused culture begins with actively engaging employees in emergency preparedness. Start by making safety procedures clear, accessible, and easy to understand. Encourage employees to participate in safety training and empower them to report hazards they identify. Open communication channels foster a proactive approach where everyone feels responsible for workplace safety. When employees are involved and informed, they become essential partners in strengthening organisational resilience.
To build resilience, regular feedback and post-incident reviews are crucial. Each emergency or drill provides insights that can improve procedures and close gaps. Gathering feedback after these events helps organisations refine their Emergency Action Plan and keep it current. Continuous improvement isn’t just about refining processes; it also reinforces the organisation’s commitment to safety, fostering a responsive and resilient culture that adapts to new risks.

A well-developed Emergency Action Plan is essential for protecting employees and maintaining business continuity. It safeguards people, reduces risks, and promotes a culture of resilience. By reviewing and improving your current plans, and considering professional support like NGS’ risk management services, your organisation can strengthen its preparedness and ensure a secure, resilient future.